
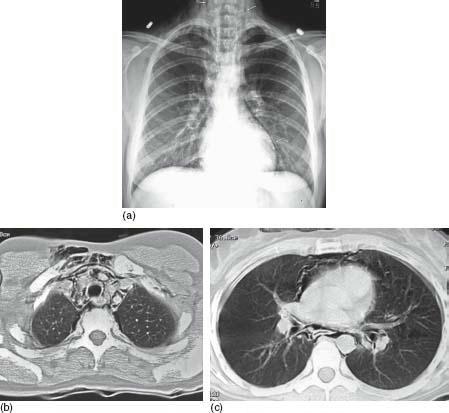
Pulmonary barotrauma (pulmonary overpressurization syndrome, POPS, or burst lung) can occur if the diver fails to expel air from the lungs during ascent.

During "bounce diving" the eustachian tube may become inflamed and lead to a middle ear squeeze. As the spray wears off during diving, tissues swell and cause obstruction, resulting in a pressure difference and damage. A reverse squeeze occurs in the middle ear or sinus when a diver has an upper respiratory infection (cold) and has used nasal spray to open the breathing passages.
When there is a problem with the tube, the middle ear volume decreases and pulls the eardrum inward, creating damage and pain. The eustachian tube is a small canal that connects the middle ear to the back part of the nasal cavities and allows pressure to equalize. Middle ear squeeze occurs when you cannot equalize the pressure in your middle ear.This can damage the tissue in the ear canal, usually your eardrum. As the water pressure increases while you descend, the air pocket between the obstruction and the tympanic membrane (eardrum) shrinks. External ear squeeze occurs when your ear canal is blocked by something such as earplugs or earwax.However, if a diver ascends too quickly, nitrogen gas bubbles will form in body tissue rather than being exhaled. Because of the water pressure, body tissue absorbs nitrogen gas faster as a diver descends than when ascending to the surface. Decompression sickness, or "the bends," is related more to Henry's Law, which states that more gas will be dissolved in a liquid when the gas is pressurized.As you dive deeper when scuba diving, pressure increases, and this volume change in gas-filled spaces and organs within your body accounts for the distortion and damage to surrounding tissues.

As the pressure increases, the volume decreases and vice versa. Boyle's law states that the product of the multiplication of pressure and volume remains a constant. What Facts Should I Know about Barotrauma/Decompression Sickness?īarotrauma refers to medical problems that arise from the pressure differences between areas of the body and the environment and is a particular concern for scuba divers.Ĭertain laws of physics apply to this topic.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
